How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision inspections. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and essential controls to advanced techniques and legal considerations. We’ll explore the nuances of different drone models, flight modes, and camera settings, ensuring you’re well-equipped to confidently take to the skies.
Unde
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and understanding of the controls, and a great resource for learning this is found at how to operate a drone. This website offers comprehensive guidance on safe and effective drone operation, covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques.
Ultimately, responsible operation ensures both your safety and the safety of others.
rstanding drone operation involves more than just mastering the controls; it’s about responsible piloting and adherence to safety regulations. We will delve into crucial safety protocols, legal requirements, and troubleshooting common issues, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to operate your drone responsibly and efficiently.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to strict safety procedures are paramount. This ensures the safety of yourself, others, and your drone. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents, damage, and legal repercussions.
Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection involves visually and functionally checking key components of your drone. This includes verifying battery charge levels, inspecting propellers for damage, and ensuring a strong GPS signal. Skipping even one step can compromise the safety and functionality of your flight.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Following a structured checklist minimizes the risk of overlooking critical pre-flight steps. The following table provides a sample checklist; adapt it based on your specific drone model.
| Item | Check | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Charge | Sufficient charge for planned flight time | Note remaining battery percentage. | |
| Propeller Inspection | Check for cracks, bends, or damage | Replace damaged propellers immediately. | |
| GPS Signal Strength | Verify strong signal lock | Ensure sufficient satellites are acquired. | |
| Gimbal Functionality | Test camera movement | Check for smooth and stable camera operation. | |
| Drone Body Inspection | Check for any damage or loose parts | Ensure all components are securely attached. | |
| Remote Control Batteries | Sufficient charge for planned flight time | Replace batteries if necessary. | |
| Flight Area Assessment | Identify potential hazards (obstacles, people, etc.) | Plan a safe flight path. | |
| Weather Conditions | Check for wind speed, precipitation, and visibility | Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions. |
Safety Procedures
Understanding and adhering to safety procedures is crucial for responsible drone operation. This includes identifying safe flight zones, understanding airspace regulations, and being aware of potential hazards.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart

A visual representation of the pre-flight procedure can aid in remembering each step. The flowchart would start with “Power On Drone and Controller,” followed by “Battery Check,” “Propeller Inspection,” “GPS Signal Check,” “Flight Area Assessment,” “Weather Check,” and finally, “Proceed to Flight” if all checks are satisfactory. A “No” response at any stage would lead to a troubleshooting step and a potential flight postponement.
Drone Controls and Operation
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different drones may have slightly varying control schemes, but the basic principles remain consistent. Mastering these controls allows for precise maneuvering and avoids accidents.
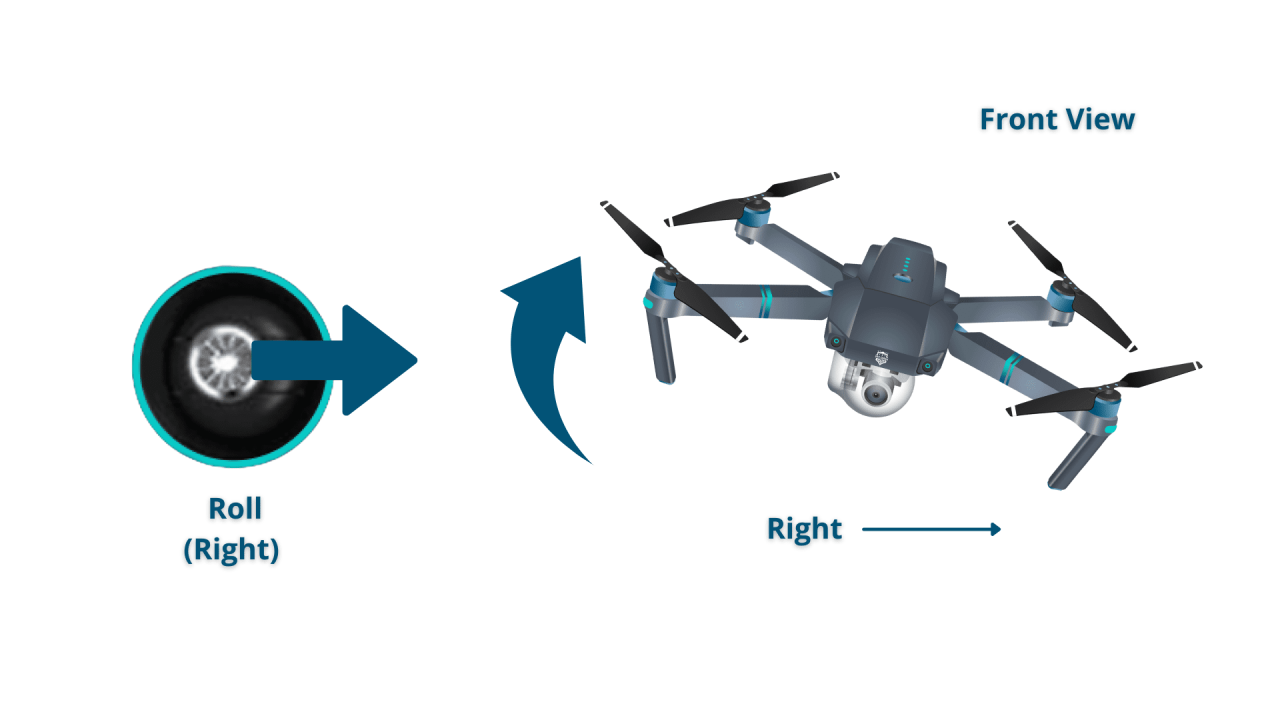
Drone Remote Control Layout
A typical drone remote controller has two joysticks, several buttons, and potentially switches. The left joystick generally controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right joystick manages pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right). Buttons often control functions like takeoff, landing, camera control, and return-to-home (RTH). A labeled diagram would illustrate these controls clearly, showing the position and function of each joystick and button.
Basic Drone Maneuvers

- Takeoff: Engage the takeoff sequence (usually a button press) to initiate a controlled ascent.
- Landing: Initiate the landing sequence (usually a button press) for a controlled descent.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air by carefully adjusting the joysticks.
- Directional Movement: Use the right joystick to control the drone’s forward, backward, left, and right movements.
- Altitude Adjustment: Use the left joystick to control the drone’s ascent and descent.
- Yaw Control: Use the left joystick to rotate the drone left or right.
Drone Control Scheme Comparison
While the fundamental principles of drone control remain consistent, minor variations exist across different drone models. Some drones may utilize different button combinations for specific functions, or their joystick responsiveness might vary. Understanding these nuances is crucial for safe and efficient operation of various models.
Smooth and Controlled Movements
Achieving smooth and controlled movements requires practice and finesse. Avoid abrupt changes in direction or altitude, as this can lead to instability and potential crashes. Gentle joystick movements and gradual adjustments are key to maintaining a stable and controlled flight.
Flight Modes and Settings
Most drones offer various flight modes and settings to tailor the flight experience to your skill level and desired outcome. Understanding these modes and how to adjust camera settings is essential for optimal performance and image quality.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, providing a more stable and forgiving flight experience. Sport mode unlocks higher speeds and more agile maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots. GPS mode uses satellite data for positioning and enables features like return-to-home (RTH).
Camera Settings Adjustment
Optimizing camera settings is crucial for capturing high-quality images and videos. Resolution determines image detail, ISO controls sensitivity to light (affecting noise levels), and shutter speed impacts motion blur. Adjusting these settings based on lighting conditions and desired effects is essential for professional-looking aerial content.
Flight Mode Comparison
| Flight Mode | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Stable, forgiving, suitable for beginners | Limited speed and maneuverability |
| Sport Mode | High speed, agile maneuvers | Requires skill and experience, less stable |
| GPS Mode | Precise positioning, RTH functionality | Requires strong GPS signal, may be less responsive in areas with weak signals |
Return-to-Home (RTH) Function
The RTH function automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point. This is a crucial safety feature, especially in case of signal loss or low battery. Proper configuration of RTH, including setting a home point and understanding its limitations, is essential for safe operation. Factors like GPS signal strength and environmental conditions can affect the reliability of RTH.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding both the technical aspects of your drone and the principles of photography and videography. This section covers techniques for high-quality content creation and post-processing.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Optimal lighting conditions are crucial for high-quality aerial photography and videography. The “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) provides soft, warm light ideal for stunning visuals. Composition is also key; utilizing the rule of thirds and leading lines can significantly improve the visual appeal of your shots.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of safety regulations and technical proficiency. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and effective drone piloting comes down to practice and understanding the fundamentals.
Utilizing Advanced Drone Features
Features like waypoint navigation allow for pre-programmed flight paths, enabling complex shots and consistent camera angles. Orbital shots, where the drone circles a subject while maintaining a constant distance and camera angle, create dynamic and engaging visuals.
File Transfer and Editing
Transferring files from your drone to a computer or mobile device is typically done via a dedicated app or SD card reader. Editing drone footage often involves stabilizing shaky footage using software like Adobe Premiere Pro or DaVinci Resolve. Techniques like color grading and adding visual effects can further enhance the quality of your videos.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful preparation, drone malfunctions can occur. Knowing how to identify and address common problems is essential for maintaining safe and efficient operation.
Common Drone Problems, How to operate a drone
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery Warning | Insufficient battery charge | Land immediately, recharge battery. |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructed GPS signal, interference | Relocate to an area with a clear view of the sky. |
| Unexpected Crash | Pilot error, mechanical failure, strong winds | Inspect drone for damage, review flight logs. |
| Motor Malfunction | Motor damage, loose connection | Inspect and repair or replace the affected motor. |
| Propeller Damage | Collision, impact | Replace damaged propellers. |
Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are vital for optimal drone performance and longevity. This includes cleaning the drone body and propellers, inspecting for damage, and lubricating moving parts (as per manufacturer recommendations).
Emergency Procedures
In case of a sudden loss of control, prioritize a safe landing. If possible, engage the RTH function. If the drone is beyond recovery, prioritize the safety of people and property in the vicinity.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local regulations and laws. This ensures safe and legal operation, avoiding potential fines or legal repercussions.
Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary significantly depending on location. Some areas may require registration, permits, or specific flight restrictions. Familiarize yourself with the specific rules and regulations in your area before operating your drone. These regulations often address airspace restrictions, flight altitudes, and operational limitations.
Restricted Airspace
Certain areas are restricted or prohibited for drone flight. These include airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. Using apps or websites that display airspace restrictions is crucial for safe and legal operation.
Permits and Licenses
Commercial drone operation often requires obtaining necessary permits and licenses. The specific requirements vary depending on the type of operation and local regulations. Researching and obtaining the appropriate permits before undertaking commercial drone activities is crucial.
Best Practices for Responsible Drone Operation
- Always check weather conditions before flying.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Fly responsibly and avoid endangering people or property.
- Adhere to all local regulations and laws.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of technical skill, responsible piloting, and a thorough understanding of relevant regulations. This guide has provided a comprehensive framework, covering pre-flight procedures, control techniques, flight modes, photography tips, troubleshooting, and legal compliance. By diligently following these guidelines and prioritizing safety, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while ensuring a responsible and enjoyable flying experience.
Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to all local regulations.
General Inquiries
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home, and intuitive controls.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model and battery size, typically ranging from 15 to 30 minutes per charge. Always carry extra batteries.
What happens if I lose the GPS signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will attempt to bring the drone back to its starting point. However, it’s crucial to practice safe flying habits and stay within visual line of sight.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures.